Table of Contents
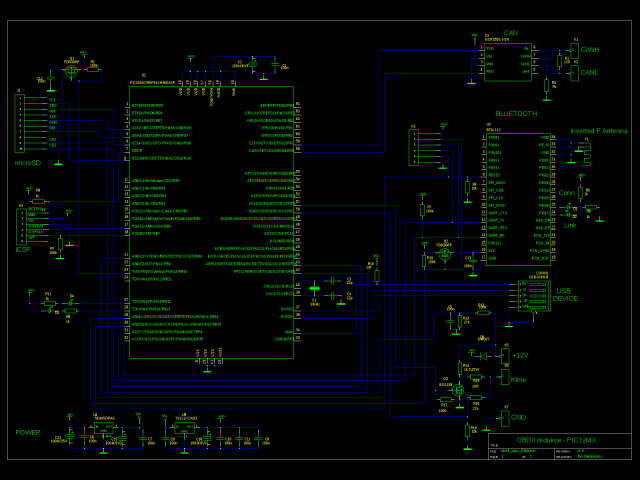
PIC32MX OBD Evaluation Board
Requirements
Basics of communication protocol
PIC module communicates with control unit via Bluetooth. In most cases communication is initiated by control unit via sending 'query' message to PIC module. Messages are composed from ASCII characters only which simplifies debugging (one can send message using any popular terminal emulator). Following is an example of query which reads value from channel 8 of A/D converter:
--------------------------------------- | SOF | ID | CMD | DATA | CHSUM | EOF | --------------------------------------- | < | A | A | 08 | EA58 | > | ---------------------------------------
where
| SOF | start of frame |
|---|---|
| ID | module ID (e.g. analog module) |
| CMD | command |
| DATA | data payload (up to 1kB of bytes, 2kB of ASCII characters ) |
| CHSUM | CRC-CCITT checksum (optional) |
| EOF | end of frame |
Packets can be amended with checksum to verify their integrity. The checksum is calculated as 16bit CRC-CCITT of ASCII codes of all ASCII characters in packet excluding SOF and EOF. This feature is turned off by default and has to be explicitly enabled - see below.
Response from PIC module can have following formats depending on the result of operation and if there is any data payload to be returned.
- command succeeded, no data payload
-------------------------------- | SOF | ID | ACK | CHSUM | EOF | -------------------------------- | < | A | A | A122 | > | --------------------------------
- command failed
-------------------------------------- | SOF | ID | NAK | ERR | CHSUM | EOF | -------------------------------------- | < | A | N | 01 | F054 | > | --------------------------------------
- command succeeded, there are data to be returned immediately in one packet
--------------------------------------- | SOF | ID | PKT | DATA | CHSUM | EOF | --------------------------------------- | < | A | 00 | 1234 | 6B45 | > | ---------------------------------------
- command succeeded, data are to be returned later in several packets
-------------------------------- --------------------------------------- --------------------------------------- | SOF | ID | ACK | CHSUM | EOF | | SOF | ID | PKT | DATA | CHSUM | EOF | | SOF | ID | PKT | DATA | CHSUM | EOF | -------------------------------- ... --------------------------------------- --------------------------------------- | < | A | D | 8523 | > | | < | A | 01 | 1234 | 6C21 | > | | < | A | 00 | 1234 | 6BFC | > | -------------------------------- --------------------------------------- ---------------------------------------
where
| SOF | start of frame |
|---|---|
| ID | module ID (e.g. A/D module) |
| PKT | packet number (00 for last packet) |
| ACK | acknowledge (A for no data payload, D for data to be sent in following packet(s)) |
| NAK | negative acknowledge |
| ERR | error code |
| DATA | data payload (up to 1kB of bytes, 2kB of ASCII characters ) |
| CHSUM | CRC-CCITT checksum |
| EOF | end of frame |
Summary of currently supported module IDs:
| A | PIC A/D converter |
|---|---|
| C | Controller Area Network (CAN) module |
| E | communication with car ECUs |
| L | Carmon logger |
| M | reserved |
| P | core PIC module |
| R | RFID module |
| Q | data acquisition module |
Generic NAK responses (shared by all modules)
| N01 | unknown module ID or command |
|---|---|
| N02 | invalid value |
| N03 | underlying module busy |
| N04 | I/O error |
| N05 | CRC error |
Following chapters provide more details about communication with particular modules.
PIC core module
PIC core module provides API for
- configuring parameters of communication with master module
- getting EEPROM parameters
- setting EEPROM parameters
- getting date and time
- setting date and time
- reading temperature sensor
- low level communication with devices on I²C bus
Commands
| c | calculate CRC checksum for given data |
|---|---|
| C | configure communication parameters |
| d | get date and time |
| D | set date and time |
| t | get temperature from MCP9801 temperature sensor |
| e | get EEPROM parameter |
| E | set EEPROM parameter |
| i | read data from I²C device |
| I | write data to I²C device |
Calculating CRC checksum
Query ---------------------------------------------- | SOF | P | c | TYPE | P1..P4 | D1..DN | EOF | ----------------------------------------------
where
| TYPE | 1b | s - 16-bit CRC-CCITT calculated by software (only P4 used); d - CRC calculated by DMA module |
|---|---|---|
| P1 | 1b | 0 - input data not reflected (MSB first); ≠0 - input data reflected (LSB first) |
| P2 | 1b | length of CRC polynom (1..32) |
| P3 | 4b | CRC polynom |
| P4 | 4b | CRC seed |
| D1..DN | Nb | data in form of ASCII HEX |
Response ------------------------------------------- | SOF | P | 00 | CRC | TIME | CHSUM | EOF | -------------------------------------------
where
| CRC | 4b | calculated CRC |
|---|---|---|
| TIME | 2b | time in μs the calculation process took |
Error codes
| N02 | Invalid parameters provided |
|---|
Configuring communication parameters
------------------------------------- | SOF | P | C | CRCEN | CHSUM | EOF | -------------------------------------
where
| CRCEN | 1 byte | != 0 - packets amended with CRC-CCITT checksum |
|---|
Error codes
| EINVAL | Invalid parameters provided |
|---|
Setting EEPROM parameter
------------------------------------------- | SOF | P | E | NUM | VALUE | CHSUM | EOF | -------------------------------------------
where
| NUM | 1b | parameter number |
|---|---|---|
| VALUE | Nb | parameter value |
Error codes
| EINVAL | Invalid parameter number |
|---|
Valid parameters
| num | size | description |
|---|---|---|
| 01 | 2b | PID autoscan mode - PID sample rate in [ms] |
| 02 | Nb | PID autoscan mode - PID groups |
Getting EEPROM parameter
Query ----------------------------------- | SOF | P | e | NUM | CHSUM | EOF | -----------------------------------
where
| NUM | 1b | parameter number |
|---|
Response -------------------------------------- | SOF | P | 00 | VALUE | CHSUM | EOF | --------------------------------------
where
| VALUE | Nb | parameter value |
|---|
Error codes
| EINVAL | Invalid parameter number |
|---|
Setting date and time
------------------------------------------------------------- | SOF | P | D | YYYY | MM | DD | hh | mm | ss | CHSUM | EOF | -------------------------------------------------------------
where
| YYYY | 4 chars | year |
|---|---|---|
| MM | 2 chars | month (01 to 12 where January = 01) |
| DD | 2 chars | day of month (01 to 31) |
| hh | 2 chars | hours since midnight (00 to 23) |
| mm | 2 chars | minutes after the hour (00 to 59) |
| ss | 2 chars | seconds after the minute (00 to 61), allows for up to two leap seconds |
Error codes
| EINVAL | Failed to set the date or time - provided date or time invalid |
|---|
Getting date and time
Query ----------------------------- | SOF | P | d | CHSUM | EOF | -----------------------------
Response -------------------------------------------------------------------- | SOF | P | 00 | YYYY | MM | DD | hh | mm | ss | mmm | CHSUM | EOF | --------------------------------------------------------------------
where
| YYYY | 4 chars | year |
|---|---|---|
| MM | 2 chars | month (01 to 12 where January = 01) |
| DD | 2 chars | day of month (01 to 31) |
| hh | 2 chars | hours since midnight (00 to 23) |
| mm | 2 chars | minutes after the hour (00 to 59) |
| ss | 2 chars | seconds after the minute (00 to 59) |
| mmm | 3 chars | milliseconds (000 to 999) |
Error codes
| ?? | ?? |
|---|
Getting temperature from MCP9801 temperature sensor
Query ----------------------------- | SOF | P | t | CHSUM | EOF | -----------------------------
Response ------------------------------------- | SOF | P | 00 | TTTT | CHSUM | EOF | -------------------------------------
where
| TTTT | 2b | temperature coded as two's complement (see packet format below) |
|---|
Format of TTTT packet:
| bit# | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sign | 26 °C | 25 °C | 24 °C | 23 °C | 22 °C | 21 °C | 20 °C | 2-1 °C | 2-2 °C | 2-3 °C | 2-4 °C | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Error codes
| ?? | ?? |
|---|
Reading from I²C device
Query -------------------------------------------- | SOF | P | i | A1 | A2 | LN | CHSUM | EOF | --------------------------------------------
Response ---------------------------------------------- | SOF | P | 00 | D1 | ... | DN | CHSUM | EOF | ----------------------------------------------
where
| A1 | 1b | I²C device address |
|---|---|---|
| A2 | 1b | register address |
| LN | 1b | number of bytes to be read (0..255) |
| D1..DN | Nb | data |
Error codes
| ?? | ?? |
|---|
Writing to I²C device
Query ------------------------------------------------------- | SOF | P | I | A1 | A2 | D1 | ... | DN | CHSUM | EOF | -------------------------------------------------------
where
| A1 | 1b | I²C device address |
|---|---|---|
| A2 | 1b | register address |
| D1..DN | Nb | data to be written |
Error codes
| ?? | ?? |
|---|
Carmon logger
Carmon logger module provides API for
- configuring operating mode of Carmon logger device
- determining last sector written by Carmon logger
- reading sectors from the log device
Commands
| C | configure the module |
|---|---|
| l | get number of last sector written by Carmon logger |
| R | read blocks from the log device according to provided parameters |
| r | read subsequent blocks from the log device according to parameters previously set via 'R' command |
Configure the module
Query ------------------------------------ | SOF | L | C | MODE | CHSUM | EOF | ------------------------------------
where
| MODE | 1b | operating mode (0..configuration, 1..autonomous, 2..assisted) |
|---|
ACK response ----------------------------- | SOF | L | A | CHSUM | EOF | -----------------------------
Read sectors from the log device according to provided parameters
Query -------------------------------------------------------- | SOF | L | R | CONF | SECSTART | BLKNUM | CHSUM | EOF | --------------------------------------------------------
where
| CONF | 1b | configures how sectors are transfered to the master |
|---|---|---|
| SECSTART | 4b | number of 1st sector to be read |
| BLKNUM | 4b | number of blocks to be read |
Format of CONF word:
| bit# | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2..0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NA | NA | NA | 1/0..binary/ASCII mode | 1/0..block is/is not compressed | number of sectors in block (1-8) |
ACK response - standard ASCII mode ----------------------------------------------- | SOF | L | A | SN | B1D1..B1DN | CHSUM | EOF | ----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------------------- | SOF | L | A | SN | B2D1..B2DN | CHSUM | EOF | ----------------------------------------------- ... ----------------------------------------------- | SOF | L | A | SN | BMD1..BMDN | CHSUM | EOF | ----------------------------------------------- ACK response - binary mode --------------------------------------------------- | DLE | STX | SN | B1D1..B1DN | CHSUM | DLE | ETX | --------------------------------------------------- --------------------------------------------------- | DLE | STX | SN | B2D1..B2DN | CHSUM | DLE | ETX | --------------------------------------------------- ... --------------------------------------------------- | DLE | STX | SN | BMD1..BMDN | CHSUM | DLE | ETX | ---------------------------------------------------
where
| SN | 1b | sequence number (01-FF); incremented with each packet; useful for detection of packet loss |
|---|---|---|
| BxD1..BxDN | Nb | Xth data block (CONF[2..0] sectors) |
note: When operating in binary mode, each DLE data byte is replaced with sequence of two DLE bytes.
RFID module
RFID module provides API for
- obtaining records from RFID reader via Bluetooth interface
- manipulating records captured from RFID reader to the local permanent storage (SD card)
Commands
| E | enable sending RFID records via Bluetooth |
|---|---|
| D | disable sending RFID records via Bluetooth |
| R | read logged records |
| C | remove logged records (clean up log file - its size is truncated to zero) |
Enable sending RFID records via Bluetooth
Query ----------------------------- | SOF | R | E | CHSUM | EOF | -----------------------------
ACK response ----------------------------- | SOF | R | A | CHSUM | EOF | -----------------------------
Packets containing records from RFID reader -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | SOF | R | SN | YYYY | MM | DD | hh | mm | ss | mmm | RFID DATA | CHSUM | EOF | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
where
| SN | sequence number (01-FF); incremented with each packet; useful for detection of packet loss |
|---|---|
| YYYY - mmm | timestamp of RFID record (with 1 millisecond resolution) |
| RFID DATA | RFID record (12 ASCII HEX characters) |
Disable sending RFID records via Bluetooth
Query ----------------------------- | SOF | R | D | CHSUM | EOF | -----------------------------
ACK response ----------------------------- | SOF | R | A | CHSUM | EOF | -----------------------------
Read logged records one-by-one
Logged records are read from log device one by one. The reading process is initiated by “Read the first record” query. Response to that query contains the first logged record. Subsequent records are then returned as responses to “Read next record” queries. Response with no data payload indicates that all records have been read. The whole reading process can be restarted by sending “Read the first record” query again.
"Read the first record" query -------------------------------- | SOF | R | R | F |CHSUM | EOF | --------------------------------
"Read next record" query -------------------------------- | SOF | R | R | N |CHSUM | EOF | --------------------------------
Response containing logged record -------------------------------------------------------- | SOF | R | 00 | TIMESTAMP1 | RFID DATA1 | CHSUM | EOF | --------------------------------------------------------
where
| TIMESTAMPx | timestamp of RFID record (YYYY - mmm) |
|---|---|
| RFID DATAx | RFID record (12 ASCII HEX characters) |
Response with no data payload ------------------------------ | SOF | R | 00 | CHSUM | EOF | ------------------------------
Valid NAK responses
| RN03 | module currently busy either reading or writing (due to just received tag ID) a record |
|---|
Read all logged records at once
In this case, log device sends all logged records at once. The process is initiated by “Read all records” query. The log device then sends all logged records, followed by one empty record indicating that all records have been sent. Each log record contains 8bit sequence number - the first record has sequence number set to '01', then it is incremented for each subsequent record. Once the sequence number reaches 'FF', it rolls over to '01'. '00' identifies the last record.
"Read all records" query -------------------------------- | SOF | R | R | A |CHSUM | EOF | --------------------------------
Response containing logged records -------------------------------------------------------- | SOF | R | 01 | TIMESTAMP1 | RFID DATA1 | CHSUM | EOF | -------------------------------------------------------- -------------------------------------------------------- | SOF | R | 02 | TIMESTAMP2 | RFID DATA2 | CHSUM | EOF | -------------------------------------------------------- ... ------------------------------ | SOF | R | 00 | CHSUM | EOF | ------------------------------
where
| TIMESTAMPx | timestamp of RFID record (YYYY - mmm) |
|---|---|
| RFID DATAx | RFID record (12 ASCII HEX characters) |
Valid NAK responses
| RN03 | module currently busy either reading or writing (due to just received tag ID) a record |
|---|
Delete logged records
Query ----------------------------- | SOF | R | C | CHSUM | EOF | -----------------------------
ACK response ----------------------------- | SOF | R | A | CHSUM | EOF | -----------------------------
Valid NAK responses
| RN10 | module currently busy either reading or writing log record(s) |
|---|---|
| RN13 | log device not available (e.g. SD card not present) |
Analog data acquisition module
Analog data acquisition module provides mechanism for acquiring data from internal PIC A/D converter with following parameters.
- 10-bit resolution
- up to 16 analog inputs
- automatic channel scan mode
- selectable conversion trigger source
- 16-word conversion result buffer
- selectable buffer fill modes
- eight conversion result format options
The acquisition module supports
- single or continuous acquisition
- auto, normal trigger modes
- configurable trigger level and type (rising edge, falling edge)
- up to 1024 samples per one conversion cycle
- 200us-1s sample rate
Function
When acquisition is started, the module goes through the following steps.
- acquires pre-trigger number of samples
- continues with data acquisition waiting for trigger condition to occur
- detects the trigger condition
- acquires post-trigger number of samples
Commands
| C | set parameters of acquisition (trigger mode, sample rate, …) |
|---|---|
| R | run acquisition |
| S | stop acquisition |
Configuration of acquisition mode
------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | SOF | Q | C | CH | AM |TM | TE | TP | SR | RR | PREN | POSTN | CHSUM | EOF | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
where
| CH | 1b | channel |
|---|---|---|
| AM | 1b | acquisition mode (1 - single, 2 - continuous) |
| TM | 1b | trigger mode (1 - normal, 2 - auto (do not wait for trigger)) |
| TE | 1b | trigger event (1 - rising edge, 2 - falling edge) |
| TP | 2b | trigger parameters, depends on TE |
| SR | 2b | sample rate in form of 0xvvvu (where u: 0-us, 1-ms, 2-s) |
| RR | 2b | refresh rate in form of 0xvvvu (where u: 0-us, 1-ms, 2-s) |
| PREN | 2b | number of pre-trigger samples (0x0000..0x0400) |
| POSTN | 2b | number of post-trigger samples (0x0000..0x0400) |
Error codes
| EINVAL | Configuration invalid (e.g. some of provided parameters is out of range |
|---|
If running in 'auto' trigger mode, all acquired data are returned. In 'normal' trigger mode, summary of pre-trigger and post-trigger number of samples is returned. However, if number of pre-trigger samples is set to zero, then all acquired data are returned.
Run acquisition
----------------------------- | SOF | Q | R | CHSUM | EOF | -----------------------------
Error codes
| 01 | ?? |
|---|---|
| 02 | ?? |
Stop acquisition
----------------------------- | SOF | Q | S | CHSUM | EOF | -----------------------------
Error codes
| 01 | ?? |
|---|---|
| 02 | ?? |
Post processing module
Post processing module operates on data acquired by data acquisition module.
Configuration of post processing
--------------------------------------- | SOF | Q | P | M | PAR | CHSUM | EOF | ---------------------------------------
where
| M | 1b | ID of post processing module to be activated |
|---|---|---|
| PAR | xb | parameters specific to selected post processing module |
Error codes
| EINVAL | Configuration invalid (e.g. unknown ID of post processing module |
|---|
Turn off post processing
---------------------------------- | SOF | Q | P | 00 | CHSUM | EOF | ----------------------------------
Signal identification post processing module
Collects various characteristics of acquired signal
Activate -------------------------------------- | SOF | Q | P | 02 | A | CHSUM | EOF | --------------------------------------
Format of data response -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | SOF | Q | 00 | MEAN | RMS | MIN | MAX | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | CHSUM | EOF | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
where
| MEAN | 2b | mean value |
|---|---|---|
| RMS | 2b | square of RMS value of AC part of signal |
| MIN | 2b | minimum of AC part of signal |
| MAX | 2b | maximum of AC part of signal |
| F1 - F5 | 20b | frequencies of spectrum of acquired signal in form of <F(2b)MAG(2b)> |
FFT post processing module
Performs FFT on test signal or signal acquired from A/D converter.
Activate ---------------------------------------------- | SOF | Q | P | 01 | A | LOG2N | CHSUM | EOF | ----------------------------------------------
where
| LOG2N | 1b | logarithm base 2 of the number of samples: N = 2^LOG2N |
|---|
Test FFT post processing --------------------------------------------- | SOF | Q | P | 01 | T | DATA | CHSUM | EOF | ---------------------------------------------
where
| DATA | Nb | data used to calculate FFT |
|---|
Controller Area Network (CAN) module
Commands/responses
| A | analyze the bus |
|---|---|
| C | configure the module |
| s | obtain status of the module |
| S | send packet |
| R | packet received |
Analyzing bus traffic
When attaching a node to the CAN bus we don't know much about, it is better to analyze the existing bus parameters as well as traffic before the node is allowed to actively participate in communication. Or, we may just want to take a look at what's happening on some CAN bus. As an example, modern cars use CAN bus to interconnect different electronic units and we may want to poke around - just out of curiosity. This is what analyzer mode is supposed to serve for. Following is generic packet format when working with analyzer.
------------------------------------------- | SOF | C | A | MODE | DATA | CHSUM | EOF | -------------------------------------------
where
| MODE | 1b | mode of analysis |
|---|---|---|
| DATA | xx | data specific to particular mode |
Currently supported modes:
| 00 | finish current analysis, generate report |
|---|---|
| 01 | generic snoop mode |
| 02 | address analysis |
| 03 | data analysis |
| 04 | timing analysis |
Deactivating analyzer
Analyzer is deactivated by following packet:
---------------------------------- | SOF | C | A | 00 | CHSUM | EOF | ----------------------------------
Mode 01 - generic snoop mode
In this mode, all received CAN frames are immediately passed to master. It is possible to configure which part of frames are to be sent to master. That is useful in scenarios when we are interested just in particular information (e.g. IDs or data payload). This mode honors previously configured acceptance filter, so it is possible to focus on CAN frames with particular ID. Complete format of CAN frame sent to master:
-------------------------------------------------------------------- | SOF | C | R | 00 | TSTAMP | TYPE | ID | DLC | DATA | CHSUM | EOF | --------------------------------------------------------------------
where
| TSTAMP | 2b | timestamp |
|---|---|---|
| TYPE | 1b | message type (bit 0 - RTR (1 for remote frame), bit 1 - EID (1 for extended ID) |
| ID | 4b | 29-bit extended (TYPE[1] == 1) or 11-bit standard (TYPE[1] == 0) identifier |
| DLC | 1b | data length code - 0..8 |
| DATA | 0..8b | data |
Mode is activated in following way:
----------------------------------------- | SOF | C | A | 01 | MASK | CHSUM | EOF | -----------------------------------------
where
| MASK | 1b | Bitmask selecting which information is sent to master. Active if set to 1. |
|---|---|---|
| bit 0 - TSTAMP | ||
| bit 1 - TYPE | ||
| bit 2 - ID | ||
| bit 3 - DLC | ||
| bit 4 - DATA |
Error codes
| ? | ? |
|---|
Mode 02 - address analysis
This mode is used to obtain information about IDs appearing on the bus. Once activated, it starts listening to CAN bus and sends all new IDs found to the master. This mode honors previously configured acceptance filter, so it is possible to focus on CAN frames with just particular set of IDs. Up to 100 addresses are scanned. Format of CAN frame sent to master:
--------------------------------------- | SOF | C | R | 00 | ID | CHSUM | EOF | ---------------------------------------
where
| ID | 4b | 29-bit extended or 11-bit standard identifier; all ones if ID buffer is full |
|---|
Mode is activated in following way:
---------------------------------- | SOF | C | A | 02 | CHSUM | EOF | ----------------------------------
Error codes
| ? | ? |
|---|
Mode 03 - data analysis
The next step of this drill-down type of analysis is trying to determine what kind of information particular data carry. To help with that, data analysis mode provides for possibility to focus on particular frame and analyzing changes in its data payload. The goal is to associate those changes with changes in real world (e.g. change in speedometer value). Frame is sent to master only if change in specified portion of data payload is detected. Format of CAN frame sent to master:
---------------------------------------------- | SOF | C | R | 00 | ID | DATA | CHSUM | EOF | ----------------------------------------------
where
| ID | 4b | 29-bit extended or 11-bit standard identifier |
|---|---|---|
| DATA | 0..8b | data payload |
Mode is activated in following way:
----------------------------------------- | SOF | C | A | 03 | MASK | CHSUM | EOF | -----------------------------------------
where
| MASK | 8b | Bitmask selecting which bits of data payload are undergoing process of comparison. One means particular bit participates in the process. |
|---|
Error codes
| ? | ? |
|---|
Mode 04 - timing analysis
Timing analysis provides information about timing situation on the bus. In particular, it calculates total number of frames received during analysis as well as minimum and maximum time between two subsequent frames. That mode can be either used to obtain overall picture about load on the bus or (with combination of the filtering) it is possible to collect information about frames with just particular ID - e.g. frame rate as well as jitter can be determined. To commence the analysis, following frame is to be sent to master:
---------------------------------- | SOF | C | A | 04 | CHSUM | EOF | ----------------------------------
Once the analysis is finished by deactivation packet (see above), results are sent to master in following form:
---------------------------------------------------------- | SOF | C | 00 | FNUM | TTIME | TMIN | TMAX |CHSUM | EOF | ----------------------------------------------------------
where
| FNUM | 4b | number of frames received |
|---|---|---|
| TTIME | 2b | total time of analysis - resolution 1ms |
| TMIN | 2b | minimum time between packets - resolution 100us |
| TMAX | 2b | maximum time between packets - resolution 100us |
Error codes
| ? | ? |
|---|
Module configuration
---------------------------------------------- | SOF | C | C | NUM | CFG DATA | CHSUM | EOF | ----------------------------------------------
where
| NUM | 1b | Configuration number |
|---|---|---|
| CFG DATA | xx | configuration data specific to particular configuration number |
Error codes
| ? | ? |
|---|
Configuration #1
Configures communication mode and speed.
------------------------------------------------- | SOF | C | C | 01 | MODE | SPEED | CHSUM | EOF | -------------------------------------------------
where
| MODE | 1b | 0 - normal, 1 - disabled, 2 - loopback, 3 - listen only, 4 - listen all messages |
|---|---|---|
| SPEED | 1b | 0 - 1Mbit, 1 - 500kbit, 2 - 250kbit, 3 - 125kbit |
Error codes
| ? | ? |
|---|
Configuration #2
Configures acceptance filter and mask. The CAN network is a broadcast type of network. A message transmitted by one node is received by all nodes in the network. Individual CAN nodes require a filtering mechanism to receive messages of interest. This filtering mechanism is provided by the CAN message acceptance filter and mask. Filtering is performed on the ID field of the CAN message.
--------------------------------------------------------- | SOF | C | C | 02 | MODE | FILTER | MASK | CHSUM | EOF | ---------------------------------------------------------
where
| MODE | 1b | bit 0 - if set, message type (specified via bit 1) is also compared; if cleared, bit 1 is ignored and both SID and EID messages can be received |
|---|---|---|
| bit 1 - if cleared, SID messages are received; if set, EID messages are received | ||
| FILTER | 4b | SID (EID) to be accepted |
| MASK | 4b | specifies which ID bits should be compared (0 - particular bit is not compared) |
Error codes
| ? | ? |
|---|
Obtaining module status
Query ----------------------------- | SOF | C | s | CHSUM | EOF | -----------------------------
Response -------------------------------------------------------------------- | SOF | C | 00 | ERRSTS | TERRCNT | RERRCNT | RXDROP | CHSUM | EOF | --------------------------------------------------------------------
where
| ERRSTS | 1b | Error state |
|---|---|---|
| RXOVF (bit 6) - Receive buffer overflowed | ||
| TXBO (bit 5) - Transmitter in Error State Bus OFF (TERRCNT ≥ 256) | ||
| TXBP (bit 4) - Transmitter in Error State Bus Passive (TERRCNT ≥ 128) | ||
| RXBP (bit 3) - Receiver in Error State Bus Passive (RERRCNT ≥ 128) | ||
| TXWARN (bit 2) - Transmitter in Error State Warning (128 > TERRCNT ≥ 96) | ||
| RXWARN (bit 1) - Receiver in Error State Warning (128 > RERRCNT ≥ 96) | ||
| EWARN (bit 0) - Transmitter or Receiver is in Error State Warning | ||
| TERRCNT | 1b | Transmit error counter |
| RERRCNT | 1b | Receive error counter |
| RXDROP | 1b | Number of packets dropped (not sent to master) due to high load on CAN bus |
Sending a packet
Query ------------------------------------------------------ | SOF | C | S | TYPE | ID | DLC | DATA | CHSUM | EOF | ------------------------------------------------------
Ack response ----------------------------- | SOF | C | A | CHSUM | EOF | -----------------------------
where
| TYPE | 1b | message type (bit 0 - RTR (1 for remote frame), bit 1 - EID (1 for extended ID) |
|---|---|---|
| ID | 4b | 29-bit extended (TYPE[1] == 1) or 11-bit standard (TYPE[1] == 0) identifier |
| DLC | 1b | data length code - 0..8 |
| DATA | 0..8b | data |
Error codes
| ? | ? |
|---|
Module for communication with ECUs
Commands
| C | set communication parameters |
|---|---|
| O | communication with OBD module |
Communication with OBD module
------------------------------------------- | SOF | E | O | MODE | PARS | CHSUM | EOF | -------------------------------------------
where
| MODE | 1b | OBD mode |
|---|---|---|
| PARS | Nb | parameters - mode specific |
Error codes
| ? | ? |
|---|
Configure OBD module
Query ----------------------------------------- | SOF | E | O | C | PROTO | CHSUM | EOF | -----------------------------------------
where
| PROTO | 1b | communication protocol |
|---|---|---|
| 0 - auto | ||
| 1 - KWP2000 normal | ||
| 2 - KWP2000 debug | ||
| 3 - KWP2000 combined with CAN (CAN must be configured via CAN specific commands) | ||
| 4 - CAN SID (11-bit identifier) 250 kbit | ||
| 5 - CAN SID 500 kbit | ||
| 6 - CAN EID (29-bit identifier) 250 kbit | ||
| 7 - CAN EID 500 kbit |
Response --------------------------------- | SOF | E | C | A | CHSUM | EOF | ---------------------------------
Show current data (read value of OBD PID)
Query ---------------------------------------------- | SOF | E | O | P | MODE | PID | CHSUM | EOF | ----------------------------------------------
where
| MODE | 1b | OBD mode - 0x01 for standard OBD PIDs, 0x21 for Toyota specific PIDs, … |
|---|---|---|
| PID | 1b | OBD PID |
Response ----------------------------------------------- | SOF | E | P | 00 | PID | DATA | CHSUM | EOF | -----------------------------------------------
where
| PID | 1b | OBD PID |
|---|---|---|
| DATA | Nb | OBD PID value |
Show current data periodically for given list of PIDs
Query -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | SOF | E | O | p | SR | NF | NM | NS | LIST F | LIST M | LIST S | CHSUM | EOF | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
where
| SR | 2b | sample rate in [ms] |
|---|---|---|
| NF | 1b | number of PIDs in 'fast' group |
| NM | 1b | number of PIDs in 'medium' group |
| NS | 1b | number of PIDs in 'slow' group |
| LIST F,M,S | Nb | list of PIDs for particular group |
Response ----------------------------------------------- | SOF | E | p | SN | PID | DATA | CHSUM | EOF | -----------------------------------------------
where
| SN | 1b | sequence number (01-FF); incremented with each packet; useful for detection of packet loss |
|---|---|---|
| PID | 1b | PID number |
| DATA | Nb | PID value |
Stop showing current data periodically for previously given list of PIDs
Query --------------------------------- | SOF | E | O | p | CHSUM | EOF | ---------------------------------
Response ----------------------------- | SOF | E | A | CHSUM | EOF | -----------------------------
Show Freeze Frame data
Query --------------------------------------------- | SOF | E | O | F | FFN | PID | CHSUM | EOF | ---------------------------------------------
where
| FFN | 1b | Freeze Frame number |
|---|---|---|
| PID | 1b | PID number |
Response ----------------------------------------------------- | SOF | E | F | 00 | FFN | PID | DATA | CHSUM | EOF | -----------------------------------------------------
where
| FFN | 1b | Freeze Frame number |
|---|---|---|
| PID | 1b | PID number |
| DATA | Nb | PID value |
Read "confirmed" Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Obtaining the complete list of stored confirmed DTCs is two-step process. In the first step total number of stored DTCs is determined by reading current value of PID 01 - zero indicates that no DTCs were stored. After that list of DTCs is obtained by reading DTCs one by one starting from zero.
Query ---------------------------------------- | SOF | E | O | D | DTCN | CHSUM | EOF | ----------------------------------------
where
| DTCN | 1b | DTC number |
|---|
Response ---------------------------------------- | SOF | E | D | 00 | DTC | CHSUM | EOF | ----------------------------------------
where
| DTC | 2b | DTC |
|---|
Error codes
| EINVAL | DTC with specified number does not exist |
|---|
Clear/reset emission-related diagnostic information
Clears MIL, number of stored DTCs, confirmed as well as pending DTCs, freeze frame data, etc.
Query --------------------------------- | SOF | E | O | R | CHSUM | EOF | ---------------------------------
Error codes
| EIO | ECU cannot perform this operation under current conditions (e.g. engine running) |
|---|
Problems found
- there are no blocking capacitors nearby PIC - add some
- missing pull-ups on μSD card signals